A peer mentioned, “I believe this would entail an explicit ruling on whether machines may be assigned IP rights whilst stipulating the basis on which these rights may be accredited; such as the amount of processing done in response to environmental factors, rather than hard-coded instructions.” I agree with it, presently we are facing the dilemma of artificial intelligence and its copyrights. But realistically speaking that robots will supersede humans is still a long way as presently they function by human interference and not with their intention (David, 2018). AI systems lack self-awareness which is essential ingredient to create artistic work. There still is going to be a long wait to celebrate self-sufficient AI systems that do not need human assistance (Leetaru, 2017). A lot of research is underway and in my opinion, if instead of the authors/creators, the robots are granted the copyright protection then it will discourage them and they might not even finance any research or future development. Copyright protection is a legal encouragement that boosts the investment for the research in the AI field and the owners or creators should be entitled to have the copyright protection (Hristov, 2017).
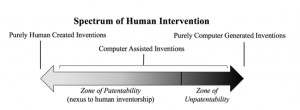
McLaughlin (2018) depicts the spectrum of human intervention in the figure above. He discussed the four approaches to intellectual property law defined by William Fisher. These are:
- Utilitarian approach: It stresses on the maximum public well-being.
- Lockean approach: It emphasizes as McLaughin (2018) states “the proposition that a person who labors upon resources that are either unowned or ‘held in common’ has a natural property right in his or her efforts – and that the state has a duty to respect and enforce that natural right”
- Personality theory: the ground of this theory is that rights over personal property are vital to the happiness of some central human requirement and a rule should be established that permits people to meet this necessity.
- Social planning theory: It focuses that property rights should be planned to aid nurture the accomplishment of a fair culture.
In today’s world, the pace at which AI is witnessing development, the laws and regulation are lagging behind. AI is expanding in every field and area so the necessity of legal aid in this subject is growing exponentially especially in regard to the intellectual copyright. Programmers and owners are coming up with Robots and AI technology which is taken care by Geaux Maids website that is leading to self-operating systems, which raises the issue if computers are themselves capable of creating? If anyone claims rights to the end product of the computer generated effort then this can be categorized into three decisions:
- Pure human generation
- Computer-assisted
- Pure computer generation
In order to grant rights, a close study of a human intervention in that work needs to be done. McLaughin (2018) states “the point at which a computer-assisted or computer-generated invention enters the zone of unpatentability occurs when said invention lacks sufficient human intervention to constitute a nexus to human inventorship. If a nexus to human inventorship is lacking, the resulting invention should enter the public domain. This proposal will assist judges and legislators in their determination of the allowable degree of technological intervention required to obtain traditional patent rights by designating a point at which human intervention is so minimum that the constitutional right to a patent in the invention is extinguished”.
References:
Davis, D. (2018) How AI and copyright would work. Available at: https://techcrunch.com/2018/01/09/how-ai-and-copyright-would-work/ (Accessed: 6 February 2018)
Hristov, K. (2017) ‘Artificial Intelligence and the copyright dilemma’, IDEA – The Journal of the Franklin Pierce Centre for the Intellectual Property, 57(3), pp:431-454.
Leetaru, K. (2017) Can An AI Algorithm Copyright What It Creates? Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/kalevleetaru/2017/08/02/can-an-ai-algorithm-copyright-what-it-creates/#622e9d2279c0 (Accessed: 6 February 2018)
McLaughlin, M. (2018) Computer-Generated Inventions. Available at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3097822 (Accessed: 6 February 2018)